一、Vue高阶
1、路由守卫(Route Guard)
路由守卫(拦截器)
在Router中的一些钩子函数,用于在导航到某个路由前或者离开当前路由前进行一些拦截和处理。
全局路由守卫
会影响所有路由
- beforeEach函数会在导航到每个路由之前被调用,可以用来进行路由拦截和权限控制;
- beforeResolve函数会在导航到每个路由之前被调用,但是在所有组件被解析之后,可以用来进行异步数据加载;
- afterEach函数会在每个路由渲染完成之后被调用,可以用来进行路由完成后的一些操作。
import Vue from 'vue'
import VueRouter from 'vue-router'
import HomeView from '../views/HomeView.vue'
Vue.use(VueRouter)
const routes = [
{
path: '/',
name: 'home',
component: HomeView
},
{
path: '/about',
name: 'about',
component: () => import(/* webpackChunkName: "about" */ '../views/AboutView.vue')
}
]
const router = new VueRouter({
mode: 'history',
base: process.env.BASE_URL,
routes
})
//全局路由守卫 前置守卫
router.beforeEach((to, from, next) => {
console.log('beforeEach,在路由切换前调用')
console.log('数据来源', from.path)
console.log('目标位置', to.path)
//放行函数
next()
})
//全局路由守卫 解析守卫
router.beforeResolve((to, from, next) => {
console.log('beforeResolve,异步路由解析完成前执行')
console.log('数据来源', from.path)
console.log('目标位置', to.path)
next()
})
//全局路由守卫 后置守卫
router.afterEach((to, from) => {
console.log('afterEach,在路由切换后调用')
console.log('数据来源', from.path)
console.log('目标位置', to.path)
})
export default router效果展示:

方法有三个参数:to、from、next。
1、to:跳转到的路由对象。
- to.path: 字符串,表示目标路由的路径
- to.name: 字符串,表示目标路由的名称
- to.fullPath: 字符串,表示目标路由的完整路径,包括查询参数和哈希值
2、from:跳转前的路由对象。
- from.path: 字符串,表示目标路由的路径
- from.name: 字符串,表示目标路由的名称
- from.fullPath: 字符串,表示目标路由的完整路径,包括查询参数和哈希值
3、next: 一个函数,调用 next 方法才能继续执行路由跳转。
- next():无参数调用 next 方法表示路由跳转成功,可以继续执行下一步路由跳转或者终止路由导航
- next(false):传递一个 false 表示终止路由导航,即取消当前的路由跳转
- next(path):传递一个路由路径,表示路由跳转到指定的路径,可以是相对路径或者绝对路径
使用全局路由守卫:
sessionStorage是HTML5提供的一种客户端存储数据的方法。它允许在浏览器中存储键/值对,并且只在当前会话中可用。也就是说,只要用户在浏览器中打开当前窗口或标签页,sessionStorage就会一直保留,但在关闭窗口或标签页时会被销毁。可以使用JavaScript的API来访问和操作sessionStorage中的数据。
在router/index中编写路由守卫:
//全局路由守卫 前置守卫
router.beforeEach((to, from, next) => {
//如果访问的是登录页(to.path= /login)直接放行
if (to.path === '/login') {
console.log('登录页')
next()
return //结束后续的所有操作
}
//如果不是登录页 判断是否登录
const token = sessionStorage.getItem('token')
//token如果不存在返回 undefined
// 0 undefined NaN 都是false
if (!token) {
//没有登录 跳转到登录页面
next('/login')
return //结束后续的所有操作
}
//如果登录了就放行
next()
})做登录页:
<template>
<div id="login">
<h1>用户登录</h1>
<div>
<label>
用户名:
<input type="text" v-model="user.username">
</label>
<label>
密码:
<input type="password" v-model="user.password">
</label>
</div>
<button @click="login">登录</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "login",
data() {
return {
user: {
username: '',
password: ''
}
}
},
methods: {
login() {
console.log('login')
//模拟用户登录
if (this.user.username === 'admin' && this.user.password === '123456') {
//登录 成功 把用户信息存储sessionStorage中
sessionStorage.setItem('token',this.user.username)
//登录成功后跳转到home页面
this.$router.push('/home')
}
}
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>注册路由:
{
path: '/login',
name: 'Login',
component: Login
}效果展示:

路由独享守卫
只影响特定路由
使用beforeEnter函数来定义,只会对当前路由生效。
在login路由中添加路由独享守卫:
{
path: '/login',
name: 'LoginView',
component: LoginView,
//路由独享守卫 只对login这一个路由起作用
beforeEnter: (to, from, next) => {
// 在访问/login之前执行
console.log('路由独享守卫生效')
next()
}
}组件内守卫
只有在某个组件被渲染时才会调用的守卫函数
- beforeRouteEnter函数在路由进入当前组件时被调用,但是在组件实例创建之前,因此无法访问this;
- beforeRouteUpdate函数在组件的路由发生变化时被调用,可以用来响应路由变化;
- beforeRouteLeave函数在路由将要离开当前组件时被调用,可以用来进行一些用户确认操作等。
home页添加组件内路由:
<template>
<div class="home">
<h1>网站首页</h1>
<nav>
<!--声明式路由:使用router-link标签来导航-->
<router-link to="/home/a">A页面</router-link>
|
<router-link to="/home/b">B页面</router-link>
|
<router-link to="/home/c">C页面</router-link>
</nav>
<!-- 显示路由组件 -->
<router-view/>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'HomeView',
beforeRouteEnter(to, from, next) {
console.log('beforeRouteEnter,在渲染该组件前调用')
next()
},
beforeRouteUpdate(to, from, next) {
console.log('beforeRouteUpdate,在当前路由发送变化调用,该组件会被反复调用')
next()
},
beforeRouteLeave(to, from, next) {
console.log('beforeRouteLeave,离开该组件对应的路由时调用')
next()
}
}
</script>
<style>
.home h1 {
color: red;
}
</style>
2、Vuex
为Vue.js应用程序开发的状态管理模式,它通过集中管理应用程序中的所有组件的共享状态
核心概念有:state(状态)、actions(操作)、mutations(变更)和 getters(获取器)
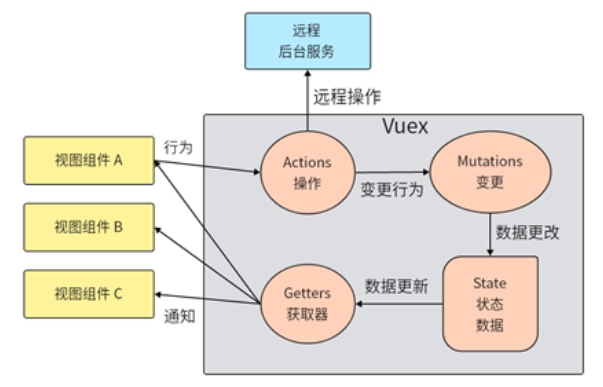
State 对象包含了应用程序的状态,并与所有组件共享。在 Vuex 中,state 对象是一个可响应的对象,它允许 Vue.js 跟踪状态的变化。所有的组件都可以访问状态对象,并通过对其进行修改来影响应用程序的状态。
Mutations 是 Vuex 中改变状态的唯一方法。它们用于同步地更新状态对象。在一个 Mutation 中,通常会进行一些简单的计算和状态更新,以便使组件可以在状态变化时及时得到通知。
Actions 用于提交 Mutations,它们之间的关键区别在于 Mutations 不能是异步的。当需要进行异步操作时,我们应该调用异步 Action,在异步操作完成后再提交 Mutations。异步操作可能包括从服务器获取数据、执行动画效果等。
Getters 用于返回状态对象的特定部分供组件使用。Getter 可以看作是对 State 对象的计算属性。它们可以用于从 state 对象中派生出一些衍生数据。
Vue计算属性
用于处理模板中的表达式,并返回计算结果的属性
在项目中components中创建ComponentDemo.vue
<template>
<div class="computed-demo">
<h1>计算属性</h1>
<p>今天是{{ today }}</p>
<p>目标日期<input type="date" v-model="targetDate"></p>
<p>今天距离目标日期{{ targetDate }}还有{{ daysFromNow }}天</p>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "ComponentDemo",
data() {
return {
//定义目标日期
targetDate: '2025-01-01',
//今天的日期 toISOString()格式化日期 substr日期截取
today: new Date().toISOString().substr(0, 10)
}
},
computed: {
//计算属性
daysFromNow: function () {
//定义今天的日期
const today = new Date() //不用上面格式化后的日期更精确
//定义目标日期
const targetDate = new Date(this.targetDate)
//计算时间差 单位是毫秒
const timeDiff = targetDate.getTime() - today.getTime()
//将毫秒转换成天
const daysDiff = timeDiff / (24 * 60 * 60 * 1000)
//return Math.ceil(daysDiff) //向上取证
return Math.floor(daysDiff) //向下取整
}
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
.computed-demo{
border: 1px solid #ccc;
}
</style>在main.js中导入并注册组件:
import ComponentDemo from "@/components/ComponentDemo"
Vue.component("computed-demo",ComponentDemo)在App.vue中使用自定义组件:
<template>
<div id="app">
<computed-demo></computed-demo>
<nav>
<router-link to="/home">首页</router-link>
|
<router-link to="/contact">联系我们</router-link>
|
<router-link to="/system">系统配置</router-link>
</nav>
<!--显示路由组件-->
<router-view/>
</div>
</template>展示效果:

Vuex共享状态
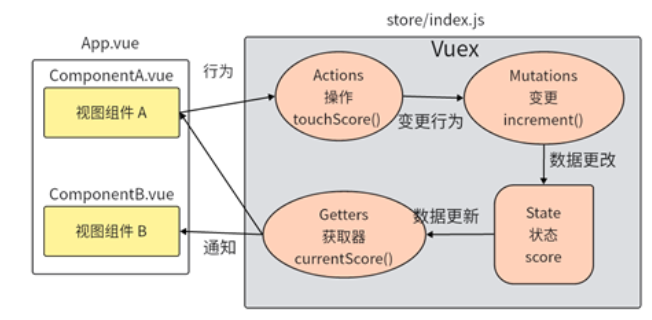
在src/store/index.js 中声明状态score和对应的行为方法
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex)
export default new Vuex.Store({
state: {
score: 0 //自定义数据
},
getters: {
//获取器 获取自定义的数据
currentScore(state) {
return state.score
}
},
//变更数据
mutations: {
//修改自定义数据
increment(state) {
state.score += 1
}
},
//操作
actions: {
touchScore(context){
console.log("修改数据")
//触发变更数据
context.commit('increment')
}
},
modules: {}
})声明A组件 src/compoment/ComponentA.vue,包含触发更新的事件按钮和显示数据状态的模板位置
<template>
<div class="computed-a">
<h1>ComputedA</h1>
<button @click="handleClick">点击+1</button>
<p>分数:{{score}}</p>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "ComputedA",
//计算属性获取state中的score
computed:{
score(){
return this.$store.getters.currentScore
}
},
methods:{
handleClick: function (){
//触发actions中的事件touchScore
this.$store.dispatch('touchScore')
}
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>main.js中注册组件
import ComputedA from "@/components/ComputedA";
Vue.component("computed-a",ComputedA)在App.vue中使用组件后效果图:

声明B组件 src/compoment/ComponentB.vue,包含显示数据状态的模板位置
<template>
<div class="computedB">
<h1>ComputedB</h1>
<p>分数:{{ score }}</p>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "ComputedB",
computed: {
score() {
return this.$store.getters.currentScore
}
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
.computedB {
border: 1px solid #aaa;
}
</style>在src/main.js中注册这个组件:
import ComputedB from "@/components/ComputedB";
Vue.component("computed-b",ComputedB)在App.vue 中引入组件A和B进行测试:
<computed-a></computed-a>
<computed-b></computed-b>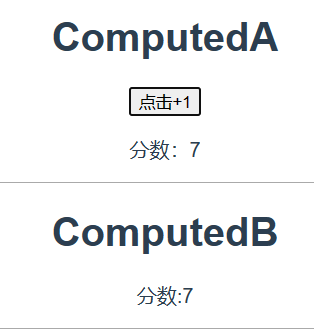
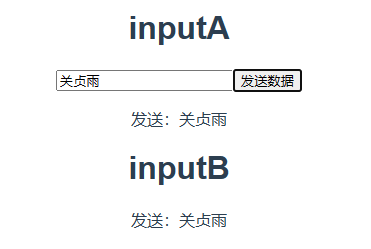
练习:将输入框中的内容共享状态
在index中编写对应的行为方法:
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex)
export default new Vuex.Store({
state: {
score: 0, //自定义数据
inputString: ''
},
getters: {
//获取器 获取自定义的数据
currentString(state) {
return state.inputString
}
},
//变更数据
mutations: {
//修改自定义数据
increment(state,textToAdd) {
state.inputString = textToAdd
}
},
//操作
actions: {
touchScore(context) {
context.commit('increment')
}
},
modules: {}
})
编写输入A:
<template>
<div class="input-a">
<h1>inputA</h1>
<input type="text" placeholder="请输入字符串" v-model="string">
<button @click="inputClick">发送数据</button>
<p>发送:{{ string }}</p>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "inputA",
data() {
return {
string: ''
}
},
computed: {
string() {
return this.$store.getters.currentString
}
},
methods: {
inputClick: function () {
const textToAdd = this.string
this.$store.commit('increment', textToAdd)
}
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>编写输出B,自定义组件并在App.vue中展示,此处省略,直接看结果:
二、项目打包部署
Vue CLI 提供了一套完整的开发和打包流程,开发者可以通过命令行工具创建项目、添加依赖、进行开发、调试、测试、打包和部署等一系列操作。
在开发阶段:
- 创建 Vue 项目:可以使用 Vue CLI 提供的 create 命令来创建一个新的 Vue 项目,例如:vue create my-project。
- 开发页面:在创建好的项目中,开发者可以使用 Vue.js 的单文件组件编写页面。
- 添加依赖:在开发过程中,可能需要添加一些第三方库或插件,可以使用 npm 或 yarn 安装这些依赖。
- 调试项目:在开发过程中,可以使用 Vue CLI 提供的 serve 命令来启动本地开发服务器,实时预览项目。
- 测试项目:Vue CLI 提供了测试工具,可以使用 test 命令来运行测试用例,例如使用 Jest 进行单元测试。
在打包阶段:
- 构建项目:在开发完成后,可以使用 build 命令将项目构建为生产环境可用的静态文件,例如:npm run build。
- 部署项目:将打包好的静态文件部署到服务器上,使用户可以访问。
