一、** final关键字
1、final修饰变量
final修饰的基本数据类型的变量可以初始化,不能再更改。
/**
* @document: final修饰变量
* @Author:SmallG
* @CreateTime:2023/7/27+9:17
*/
public class Demo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//在方法中声明的变量就是局部变量
final int a; //声明一个final的变量
a = 5; //只能赋值一次 第一次赋值成为初始化
System.out.println(a); //5
// a = 10; //编译错误 final修饰的局部变量 不能修改值
final int b =10; //在声明变量的时候同时初始化 不能再次赋值
}
}(1)final修饰局部变量
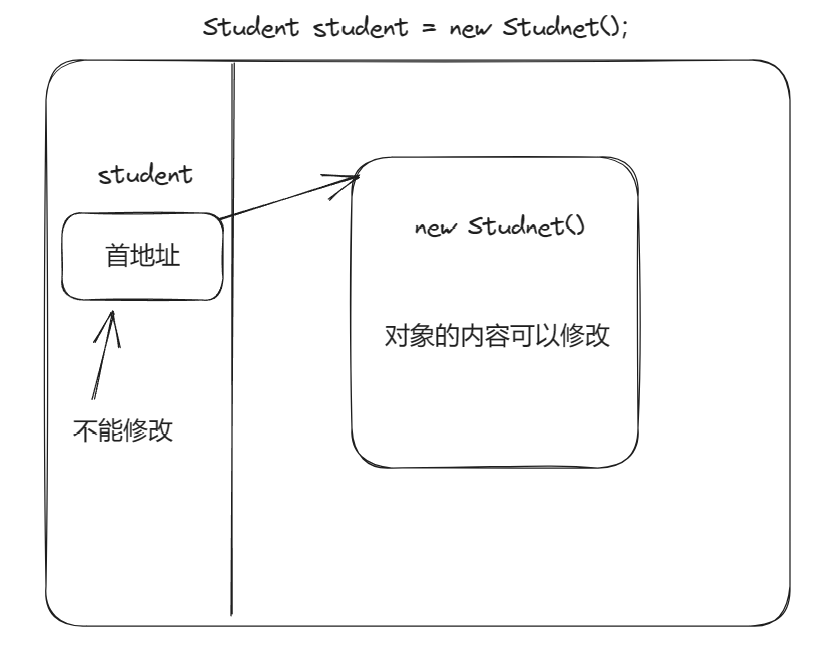
方法中的变量和方法的参数都属于局部变量。当final修饰引用类型变量时对象的首地址不能修改,但是对象的内容可以修改。
/**
* @document: final修饰局部变量
* @Author:SmallG
* @CreateTime:2023/7/27+9:17
*/
public class Demo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//在方法中声明的变量就是局部变量
//final修饰引用类型变量
//变量中存的是变量的首地址
//初始化后不能再修改
//但是变量中的值可以修改
final int[] arr = {5, 10};
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr)); //[5, 10]
arr[0] = 1;
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr)); //[1, 10]
//arr = new int [10];//报错: arr的引用不能改变
final Aoo aoo = new Aoo(); //aoo 为引用类型变量
//aoo = new Aoo(); //报错引用类型不能改变
aoo.c =10; //变量的内容可以改变
//aoo = null; //aoo引用中保存的是地址不能修改
}
}
class Aoo {
int c = 5;
}
final修饰方法的参数:
/**
* @document: final修饰方法的参数
* @Author:SmallG
* @CreateTime:2023/7/27+9:36
*/
public class Demo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Boo boo = new Boo();
boo.sum(5, 10); //在调用时进行初始化赋值
}
}
class Boo {
public void sum(int a, final int b) {
a = 10;
//b = 20; //报错:方法的参数使用final修饰 不能再次赋值
System.out.println(a + b);
}
}(2)final修饰类的成员变量
/**
* @document:final修饰类的成员属性(成员变量/实例变量)
* @Author:SmallG
* @CreateTime:2023/7/27+9:43
*/
public class Demo03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Coo coo1 = new Coo();
System.out.println(coo1.a + " " + coo1.b); //5 3
Coo coo2 = new Coo(10);
System.out.println(coo2.a + " " + coo2.b); //5 10
//coo2.a = 15; 报错:不能修改final修饰的成员属性值
}
}
class Coo {
final int a = 5; //在声明的时候直接初始化
final int b;
//不能有默认构造器 (如果非要有需要将b的值进行初始化
public Coo() {
this.b = 3;
}
public Coo(int b) {//在构造器中完成初始化
this.b = b;
}
}2、final修饰方法
final修饰的方法不能在子类中重写。
/**
* @document: final修饰方法
* @Author:SmallG
* @CreateTime:2023/7/27+10:09
*/
public class Demo04 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Doo doo = new Doo();
doo.hello(); //Hello World
SubDoo subDoo = new SubDoo();
subDoo.hello(); //Hello World
}
}
class Doo {
public final void hello() {
System.out.println("Hello World");
}
}
class SubDoo extends Doo {
//final修饰的方法可以被继承 但是不能被重写
/*public final void hello(){
报错:不能被重写
}*/
}3、final修饰类
final修饰的类不能再被继承派生出子类,在实际开发中一般禁止使用final声明类。
/**
* @document: final修饰类
* @Author:SmallG
* @CreateTime:2023/7/27+10:21
*/
public class Demo05 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Eoo eoo = new Eoo(); //可以创建相应的对象并且运行方法
eoo.hello(); //Hello World
}
}
final class Eoo {
public void hello() {
System.out.println("Hello World");
}
}
/*class Foo extends Eoo{
编译错误:被final修饰的类不能被继承
}*/二、** static关键字
1、修饰变量
成员变量有三种:实例变量、静态变量、常量
实例变量:是属于每个对象的属性,每个对象中都有一份
静态变量:是属于类的变量,只有一份,全体对象共享的同一份变量
常量:是不变的常数
静态变量:
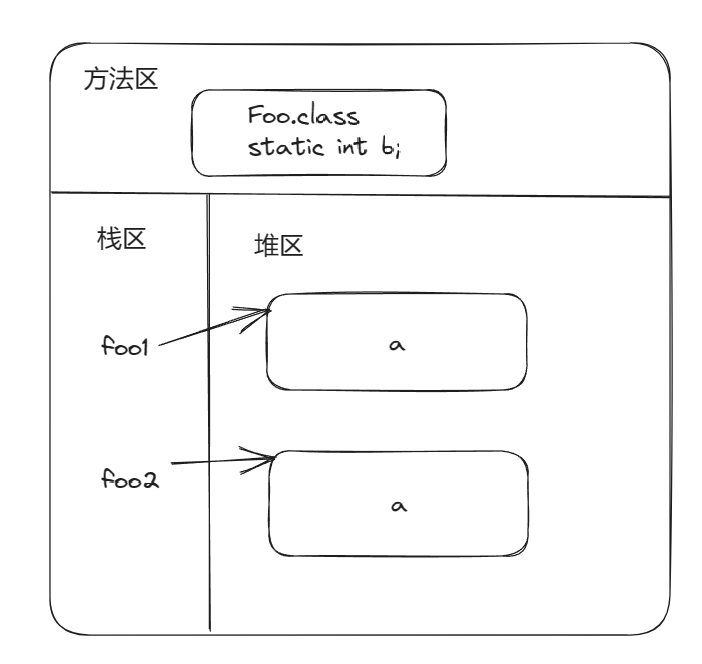
使用static修饰的变量时静态变量,全体对象共享的一份变量,用静态变量存储程序中只有一个就足够的数据,静态变量和类的信息一起存储在方法区,static不能直接修饰局部变量。
静态变量工作原理:
第一次运行时,字节码文件会被分配到方法区,类中的静态变量此时在方法区中分配出来,字节码文件只加载一次。
/**
* @document: static修饰成员属性 被修饰的属性称为静态成员 属于整个类
* 类的所有对象共享这一个数据
* @Author:SmallG
* @CreateTime:2023/7/27+10:34
*/
public class Demo06 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Foo foo1 = new Foo();
Foo foo2 = new Foo();
foo1.a = 5;
foo2.a = 10; //修改的不是一个存储位置的变量
foo1.b = 20;
foo2.b = 30; //修改的是同一个位置的变量
System.out.println(foo1.a); //5
System.out.println(foo2.a); //10
System.out.println(foo1.b); //30
System.out.println(foo2.b); //30
//static修饰的成员属性不推荐使用对象访问,推荐使用类直接访问
Foo.b = 50;
}
}
class Foo {
int a; //普通的成员属性
static int b; //static修饰的属性称为类属性/类变量 只有一份 被全体对象共享
public void hello(){
//static int age =10; static不能直接修饰局部变量
}
}
static final一起使用
同时使用时声明称为静态常量,不能被改变。
/**
* @document: 常量 static final 常量在声明的时候就赋值 以后不可修改
* @Author:SmallG
* @CreateTime:2023/7/27+11:15
*/
public class Demo07 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(Message.MSG_LOGIN_FAILED);
System.out.println(Message.MSG_LOGIN_SUCCESS);
}
}
class Message {
//用static final修饰的变量 名字采用全大写 单词组合用下划线分开
public static final String MSG_LOGIN_FAILED = "用户名或密码错误";
public static final String MSG_LOGIN_SUCCESS = "登录成功";
}常量的细节:
- 软件中不能改变的数据,应该都定义常量
- 同时使用static final修饰,两个关键字可以调换
- 常量必须初始化
- 一般常量名都是大写字母,多个单词使用下划线分割开
2、修饰方法
静态方法是属于类的方法。属于类的方法就可以直接使用类名直接引用方法。比如:Math.random()就是一个静态方法。
静态方法不能访问非静态成员,普通方法可以访问非静态成员。这里静态成员指成员属性和方法。
/**
* @document: 静态方法 使用static关键字修饰的方法 可以直接用类名访问
* @Author:SmallG
* @CreateTime:2023/7/27+14:02
*/
public class Demo08 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person.add(3, 5); //8
//成员方法只能通过对象访问
Person person = new Person("tom");
person.WhoRY();
person.add(6,9);//15 对象也可以访问静态方法 不推荐
//我是tom
//10
WaWo(); //可以直接访问本类中的静态方法
// HH(); 报错:不可以直接访问本类中的普通方法
}
public static void WaWo(){
System.out.println("这里是静态方法");
}
public void HH(){
System.out.println("这里是普通方法");
}
}
class Person {
String name;
static int num = 10;
public Person(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
//静态方法不能用this 静态方法属于整个类 this是属于对象的
//静态方法不能访问非静态成员
public static void add(int a, int b) {
System.out.println(a + b);
// System.out.println(name); 报错:静态方法不能访问非静态成员(成员属性和方法)
System.out.println(num); //10
}
public void WhoRY() {
System.out.println("我是" + this.name);
System.out.println(num); //普通方法可以访问静态成员
}
}3、static的其他用法
代码块
/**
* @document: 代码块 在类中直接使用一对{}编写的代码
* @Author:SmallG
* @CreateTime:2023/7/27+14:27
*/
public class Demo09 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Goo goo1 = new Goo(); //属性成功初始化
Goo goo2 = new Goo(); //属性成功初始化
System.out.println(goo1.name); //Tom
System.out.println(goo2.name); //Tom
}
}
class Goo {
String name;
//每次创建对象,都会调用代码块中的内容
{
name = "Tom";
System.out.println("属性成功初始化");
}
}静态代码块
在类加载期间执行,只加载一次。
/**
* @document: 静态代码块 在加载类的时候(创建类的对象或访问类的静态成员)执行 以后不再执行
* @Author:SmallG
* @CreateTime:2023/7/27+14:33
*/
public class Demo10 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建对象
/*Hoo hoo1 = new Hoo(); //静态成员初始化成功
Hoo hoo2 = new Hoo(); //静态代码块只能执行一次*/
System.out.println(Hoo.name); //静态成员初始化成功 Tom 先加载类 静态代码块立即执行
}
}
class Hoo {
static String name;
//静态代码块只能访问静态成员
static {
System.out.println("静态成员初始化成功");
name = "Tom";
}
}静态导入
import static static1.Person.*; //加载Person里面的所有组件
/**
* @document: 静态导入 在导包的时候前面加static
* @Author:SmallG
* @CreateTime:2023/7/27+15:05
*/
public class Demo11 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
eat();
sleep();
talk();
}
}三、**abstract抽象
1、抽象类
抽象类不能直接实例化创建对象,是个半成品创建对象没有意义,只包含部分的属性和方法。
abstract和final不可以同时修饰一个类,final关键字不能被继承,而抽象类如果不能被继承就没有了意义。
抽象类中可以创建构造器,用于子类的继承。
/**
* @document: 父类
* @Author:SmallG
* @CreateTime:2023/7/27+15:30
*/
//抽象类不能被实例化 但是可以被继承
public abstract class Person {
String name;
int age;
public void whoru() {
System.out.println("我是" + name);
}
}
/**
* @document:
* @Author:SmallG
* @CreateTime:2023/7/27+15:33
*/
public class Student extends Person {
public Student(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public void study() {
System.out.println("我在学习");
}
}
/**
* @document:
* @Author:SmallG
* @CreateTime:2023/7/27+15:37
*/
public class Teacher extends Person {
public Teacher(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public void teach() {
System.out.println("我在讲课");
}
}
/**
* @document:
* @Author:SmallG
* @CreateTime:2023/7/27+15:40
*/
public class Worker extends Person {
public Worker(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public void work() {
System.out.println("我在工作");
}
}
/**
* @document: 测试类
* @Author:SmallG
* @CreateTime:2023/7/27+15:42
*/
public class Demo13 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student student = new Student("Tom", 12);
//创建老师对象
Teacher teacher = new Teacher("Jerry", 30);
//创建工人对象
Worker worker = new Worker("Spike", 25);
student.whoru(); //我是Tom
student.study(); //我在学习
teacher.whoru(); //我是Jerry
teacher.teach(); //我在讲课
worker.whoru(); //我是Spike
worker.work(); //我在工作
//问题:如果创建person对象 父类没有初始化 不应该让他们创建对象
//java编译器检查 不允许创建抽象类的对象
//Person person = new Person();
//person.whoru();
}
}
2、抽象方法
使用abstract关键字声明,不包含方法体
(思想是重点)抽象方法的语法:
抽象类可以没有抽象方法,但是一个类如果有抽象方法就一定要是抽象类。子类继承抽象类要重写所有的抽象方法,否则报错。
抽象方法的意义在于便于程序的统一管理。
/**
* @document: 父类
* @Author:SmallG
* @CreateTime:2023/7/27+15:30
*/
//抽象类不能被实例化 但是可以被继承
public abstract class Person {
//抽象方法 不能有方法体
public abstract void schedule();
}
/**
* @document:
* @Author:SmallG
* @CreateTime:2023/7/27+15:33
*/
public class Student extends Person {
@Override
public void schedule() {
System.out.println("吃饭 听课");
}
}
/**
* @document: 测试类
* @Author:SmallG
* @CreateTime:2023/7/27+15:42
*/
public class Demo13 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student student1 = new Student("SmallG",23);
student.schedule();
}
}四、练习
计算汽车租赁价格
汽车租赁公司出租多种车辆,车型和租金情况如下图所示:
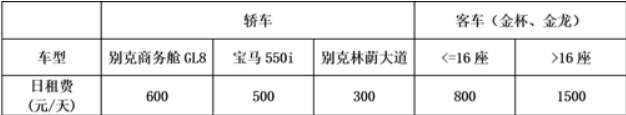
编写程序实现租赁价格的计算。
具体需求:
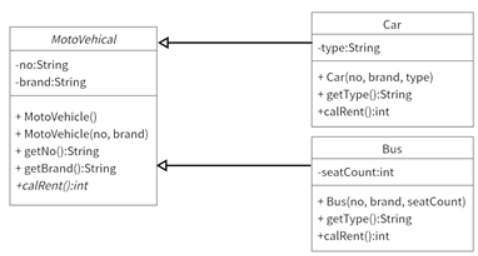
1、车辆分为轿车和客车两大类,它们都继承自抽象类MotoVehicle,如下图所示:
2、抽象类MotoVehicle
- 有参构造器:带有两个参数(String类型的汽车牌照和品牌)
- 方法getNo():返回String 类型的汽车牌照
- 方法getBrand():返回String 类型的品牌(宝马或者别克)
- 抽象方法calRent():需要一个int类型的参数表示被租赁的天数,用于计算租金
/**
* @document: 父类抽象类
* @Author:SmallG
* @CreateTime:2023/7/27+8:04
*/
public abstract class MotoVehicle {
String no; //汽车牌照
String brand; //汽车品牌
//无参构造器
public MotoVehicle() {
}
//有参构造器
public MotoVehicle(String no, String brand) {
this.no = no;
this.brand = brand;
}
//get方法
public String getNo() {
return no;
}
public String getBrand() {
return brand;
}
//抽象方法
public abstract int calRent(int days);
}3、子类 Car:表示轿车
- 有参构造器:带有三个参数(String类型的汽车牌照、品牌、车型)
- 方法getType():返回String 类型的车型(如果是宝马,则为 550i)
- 方法setType():带有Stirng类型的参数,设置车型
- 重写方法calRent():根据品牌及车型,找到对应的日租金,乘以租用天数,计算租金
/**
* @document: 汽车类,表示轿车
* @Author:SmallG
* @CreateTime:2023/7/27+8:10
*/
public class Car extends MotoVehicle {
String type;
//无参构造器
public Car() {
}
//有参构造
public Car(String no, String brand, String type) {
super(no, brand);
this.type = type;
}
public String getType() {
return type;
}
public void setType(String type) {
this.type = type;
}
@Override
public int calRent(int days) {
if (brand.equals("宝马") && type.equals("550i")) {
return days * 500;
} else if (brand.equals("别克商务舱") && type.equals("GL8")) {
return days * 600;
} else {
return days * 300;
}
}
}4、子类 Bus:表示客车
- 有参构造器:带有三个参数(String类型的汽车牌照和品牌、int类型的车座位数)
- 方法getSeatCount ():返回int 类型的车座位数
- 方法setSeatCount ():带有int 类型的参数,设置车座位数
- 重写方法calRent():根据座位数,找到对应的日租金,乘以租用天数,计算租金
/**
* @document: 表示客车
* @Author:SmallG
* @CreateTime:2023/7/27+8:17
*/
public class Bus extends MotoVehicle {
int seatCount;
public Bus() {
}
public Bus(String no, String brand, int seatCount) {
super(no, brand);
this.seatCount = seatCount;
}
public int getSeatCount() {
return seatCount;
}
public void setSeatCount(int seatCount) {
this.seatCount = seatCount;
}
@Override
public int calRent(int days) {
if (seatCount <= 16) {
return days * 800;
} else {
return days * 1500;
}
}
}5、定义测试类TestRent,并实现车辆的租赁计算。
运行效果如下所示:
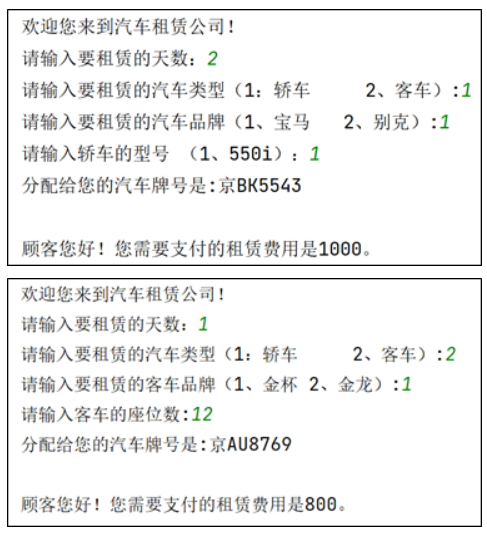
/**
* @document: 测试类
* @Author:SmallG
* @CreateTime:2023/7/27+8:20
*/
public class TestRent {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int sum = 0;
System.out.println("欢迎您来到汽车租赁公司!");
System.out.print("请输入要租赁的天数:");
int days = scanner.nextInt();
boolean s1 = true;
int num1 = 0;
while (s1) {
System.out.print("请输入要租赁的汽车类型(1:轿车\t 2、客车):");
num1 = scanner.nextInt();
if (num1 != 1 && num1 != 2) {
System.out.println("请输入正确的汽车类型!");
} else {
s1 = false;
}
}
//选择轿车
int num2 = 0;
if (num1 == 1) {
boolean s2 = true;
while (s2) {
System.out.print("请输入要租赁的汽车品牌(1、宝马\t 2、别克):");
num2 = scanner.nextInt();
if (num2 != 1 && num2 != 2) {
System.out.println("请输入正确的汽车品牌!");
} else {
s2 = false;
}
}
} else {//选择客车
boolean s4 = true;
int num5 = 0;
while (s4) {
System.out.print("请输入要租赁的客车品牌(1、金杯\t 2、金龙):");
num5 = scanner.nextInt();
if (num5 != 1 && num5 != 2) {
System.out.println("请输入正确的汽车品牌!");
} else {
s4 = false;
}
}
boolean s5 = true;
int num6 = 0;
while (s5) {
System.out.print("请输入客车的座位数:");
num6 = scanner.nextInt();
if (num6 <= 0) {
System.out.println("请输入正确的座位数!");
} else {
s5 = false;
}
}
if (num5 == 1) {
Bus bus = new Bus("京AU8769", "金杯", num6);
sum = bus.calRent(days);
System.out.println("分配给您的汽车牌号是:" + bus.no);
}else{
Bus bus = new Bus("京AU8769", "金龙", num6);
sum = bus.calRent(days);
System.out.println("分配给您的汽车牌号是:" + bus.no);
}
}
//轿车型号
boolean s3 = true;
int num3 = 0;
int num4 = 0;
if (num2 == 1) { //轿车宝马
while (s3) {
System.out.print("请输入轿车型号(1、550i):");
num3 = scanner.nextInt();
if (num3 == 1) {
s3 = false;
} else {
System.out.println("请输入正确的轿车型号!");
}
}
Car car = new Car("京BK5543", "宝马", "550i");
sum = car.calRent(days);
System.out.println("分配给您的汽车牌号是:" + car.no);
} else if (num2 ==2){//轿车别克
while (s3) {
System.out.print("请输入轿车型号(1、GL8):");
num4 = scanner.nextInt();
if (num4 == 1) {
s3 = false;
} else {
System.out.println("请输入正确的轿车型号!");
}
}
Car car = new Car("京BK5543", "别克商务舱", "GL8");
sum = car.calRent(days);
System.out.println("分配给您的汽车牌号是:" + car.no);
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println("顾客您好!您需要支付的租赁费用是" + sum + "。");
} }
